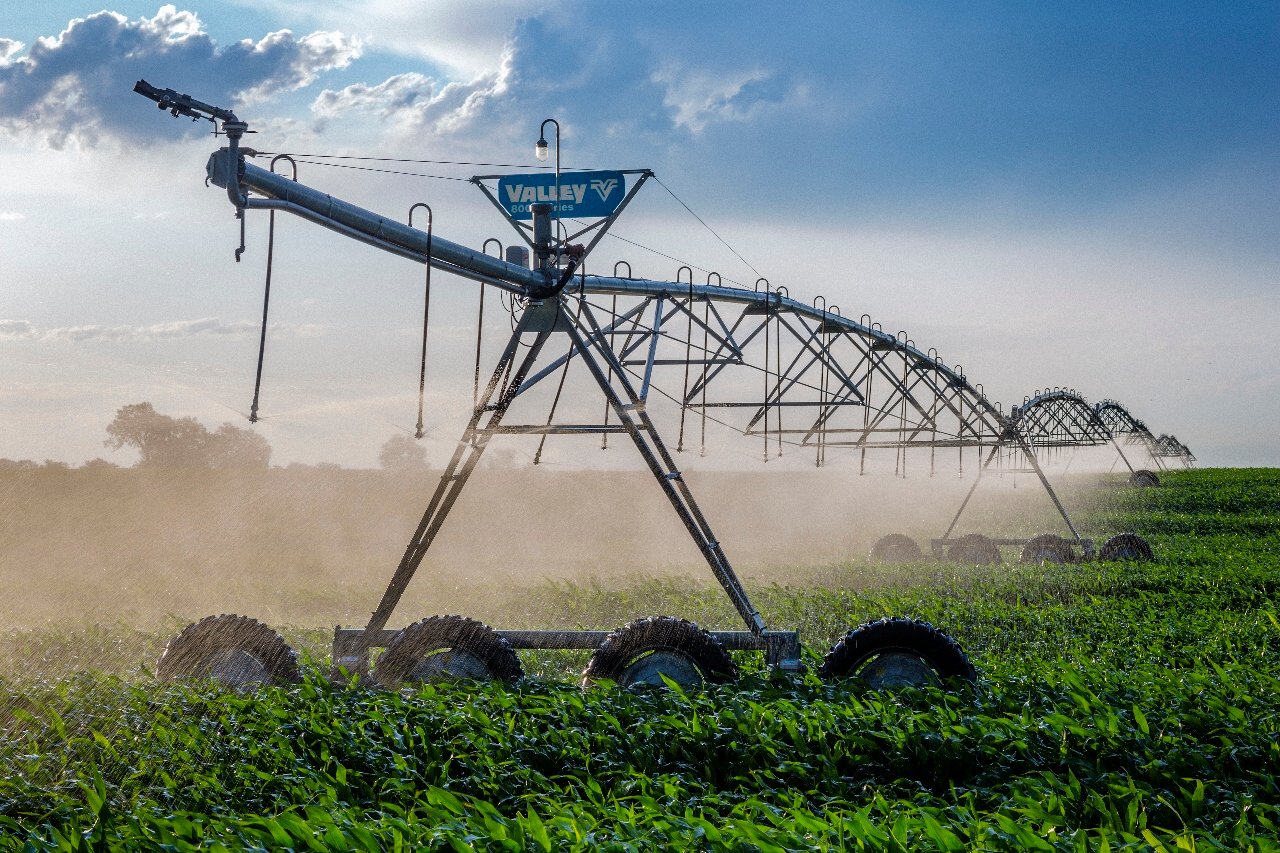

Water is an indispensable resource in agriculture, and its efficient management is critical for sustainable farming. Precision irrigation, a method that delivers the right amount of water to crops at the right time, not only conserves water but also enhances crop health and yields. This article explores the types of precision irrigation systems, their benefits, and strategies for effective implementation.
Drip Irrigation
Sprinkler Irrigation
Subsurface Irrigation
Automated Systems
Water Conservation: Targets the root zone, significantly reducing water wastage.
Enhanced Crop Health: Prevents under- or overwatering, creating optimal conditions for growth.
Cost Efficiency: Cuts water and energy costs by eliminating inefficiencies.
Soil Preservation: Reduces erosion and nutrient leaching caused by excessive water application.
Modern precision irrigation has been transformed by advancements in agricultural technology, including:
Precision irrigation not only boosts productivity but also promotes environmental sustainability by:
Drip Irrigation for Tomatoes in Sub-Saharan Africa
In water-scarce regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa, drip irrigation has become a game-changer for high-value crops like tomatoes. Farmers have achieved up to a 60% reduction in water usage while increasing yields by 30%. By delivering water directly to the root zone, this method minimizes evaporation losses, especially in arid climates, enabling sustainable farming practices.
Precision irrigation represents a paradigm shift in modern agriculture, offering an innovative solution to the challenges of water management. By adopting this sustainable approach, farmers can enhance yields, conserve water, and ensure long-term agricultural viability in a resource-constrained world.

Challenges of Wind in African Agriculture
06 Mar 2025
Elements for Plant Nutrition in African Farming
06 Mar 2025

Optimizing Greenhouse Ventilation: Balancing Temperature and Humidity for Maximum Yield
06 Mar 2025

The Role of Trellis Twine and Clips in Vertical Farming
06 Mar 2025